第1章 前言
本指南适用于瀚高数据库管理系统 V9.0。
第2章 概述
2.1.Hibernate简介
Hibernate是一个开源的对象关系映射(ORM)框架,它通过将Java对象与数据库表建立映射关系,实现了对JDBC的轻量级封装,使开发者可以以面向对象的方式来操作数据库。
2.2.Hibernate驱动包
在数据库安装目录 interfaces/jdbc 下,获得驱动jar包 hgdb-jdbc-xxx.jar。该驱动包与PostgreSQL保持兼容,其中类名、类结构与 PostgreSQL 驱动完全一致,曾经运行于 PostgreSQL 的应用程序可以直接移植到当前系统使用。
第3章 Hibernate核心接口
Hibernate有五大核心接口,分别是:Configuration、SessionFactory、Session、Transaction、Query 和 Criteria 。这五个接口构成了Hibernate运行的基本要素,可以执行存取,持久化,事务管理等操作。这五个接口可以位于系统的业务逻辑层和持久化层。
3.1.Configuration(配置接口)
作用:负责加载 Hibernate 的配置文件(如 <font style="color:rgb(64, 64, 64);">hibernate.cfg.xml</font> 或注解配置),并初始化 Hibernate 运行环境。
主要方法:
<font style="color:rgb(64, 64, 64);">configure()</font>:加载默认配置文件(<font style="color:rgb(64, 64, 64);">hibernate.cfg.xml</font>)。<font style="color:rgb(64, 64, 64);">addAnnotatedClass(Class)</font>:注册带注解的实体类。<font style="color:rgb(64, 64, 64);">buildSessionFactory()</font>:构建<font style="color:rgb(64, 64, 64);">SessionFactory</font>实例。
示例:
Configuration cfg = new Configuration().configure("hibernate.cfg.xml"); |
3.2.SessionFactory(会话工厂接口)
作用:
- 是
<font style="color:rgb(64, 64, 64);background-color:rgb(236, 236, 236);">Session</font>的工厂,线程安全,通常一个应用只需要一个<font style="color:rgb(64, 64, 64);background-color:rgb(236, 236, 236);">SessionFactory</font>(单例模式)。 - 缓存 SQL 语句、映射元数据和二级缓存数据。
主要方法:
<font style="color:rgb(64, 64, 64);background-color:rgb(236, 236, 236);">openSession()</font>:创建一个新的<font style="color:rgb(64, 64, 64);background-color:rgb(236, 236, 236);">Session</font>实例。<font style="color:rgb(64, 64, 64);background-color:rgb(236, 236, 236);">getCurrentSession()</font>:获取当前线程绑定的<font style="color:rgb(64, 64, 64);background-color:rgb(236, 236, 236);">Session</font>(需配置<font style="color:rgb(64, 64, 64);background-color:rgb(236, 236, 236);">current_session_context_class</font>)。
示例:
SessionFactory sessionFactory = cfg.buildSessionFactory(); |
3.3.Session(会话接口)
作用:
- 是 Hibernate 操作数据库的核心接口,非线程安全,每个线程应使用独立的
<font style="color:rgb(64, 64, 64);background-color:rgb(236, 236, 236);">Session</font>。 - 管理对象生命周期(CRUD 操作)。
- 提供一级缓存(Session 缓存)。
主要方法:
<font style="color:rgb(64, 64, 64);background-color:rgb(236, 236, 236);">save()</font>/<font style="color:rgb(64, 64, 64);background-color:rgb(236, 236, 236);">persist()</font>:保存对象。<font style="color:rgb(64, 64, 64);background-color:rgb(236, 236, 236);">get()</font>/<font style="color:rgb(64, 64, 64);background-color:rgb(236, 236, 236);">load()</font>:加载对象(<font style="color:rgb(64, 64, 64);background-color:rgb(236, 236, 236);">get</font>立即查询,<font style="color:rgb(64, 64, 64);background-color:rgb(236, 236, 236);">load</font>延迟加载)。<font style="color:rgb(64, 64, 64);background-color:rgb(236, 236, 236);">update()</font>/<font style="color:rgb(64, 64, 64);background-color:rgb(236, 236, 236);">merge()</font>:更新对象。<font style="color:rgb(64, 64, 64);background-color:rgb(236, 236, 236);">delete()</font>:删除对象。<font style="color:rgb(64, 64, 64);background-color:rgb(236, 236, 236);">beginTransaction()</font>:开启事务。<font style="color:rgb(64, 64, 64);background-color:rgb(236, 236, 236);">createQuery()</font>:创建 HQL 查询。
示例:
Session session = sessionFactory.openSession(); |
3.4.Transaction(事务接口)
作用:
- 封装底层事务(JDBC 或 JTA),提供统一的事务管理 API。
- 默认不自动提交,需显式调用
<font style="color:rgb(64, 64, 64);background-color:rgb(236, 236, 236);">commit()</font>或<font style="color:rgb(64, 64, 64);background-color:rgb(236, 236, 236);">rollback()</font>。
主要方法:
<font style="color:rgb(64, 64, 64);background-color:rgb(236, 236, 236);">commit()</font>:提交事务。<font style="color:rgb(64, 64, 64);background-color:rgb(236, 236, 236);">rollback()</font>:回滚事务。
示例:
Transaction tx = session.beginTransaction(); |
3.5.Query 和 Criteria(查询接口)
- Query(HQL查询接口)
作用:
- 执行 HQL(Hibernate Query Language)查询,类似 SQL 但面向对象。
主要方法:
<font style="color:rgb(64, 64, 64);background-color:rgb(236, 236, 236);">list()</font>:返回查询结果列表。<font style="color:rgb(64, 64, 64);background-color:rgb(236, 236, 236);">uniqueResult()</font>:返回唯一结果。<font style="color:rgb(64, 64, 64);background-color:rgb(236, 236, 236);">setParameter()</font>:设置参数。
示例:
Query query = session.createQuery("FROM User WHERE name = :name"); |
- Criteria(条件查询接口,已弃用,推荐 JPA CriteriaQuery)
作用:
- 提供面向对象的动态查询方式(无需写 HQL)。
示例:
Criteria criteria = session.createCriteria(User.class); |
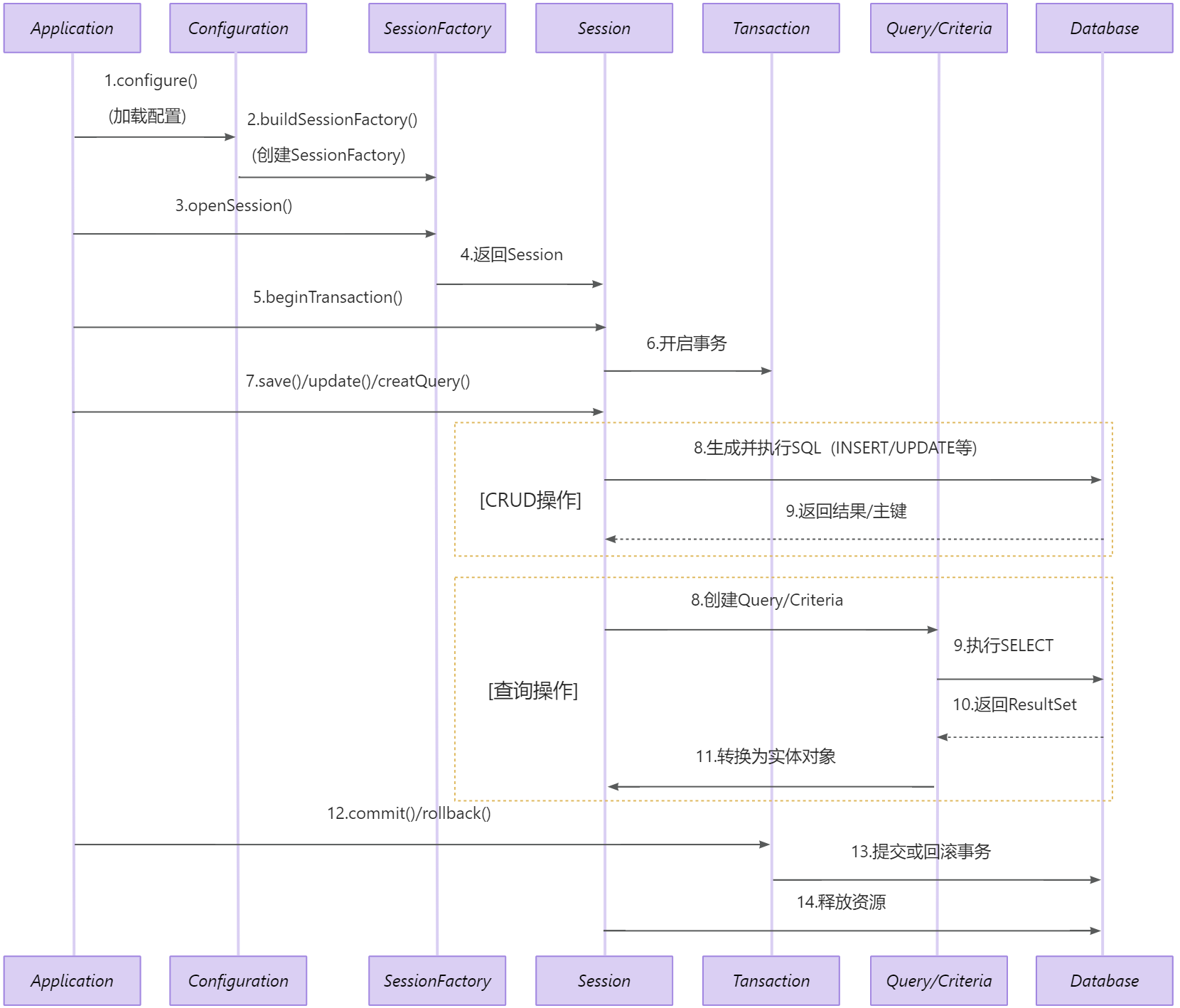
第4章 Hibernate工作流程
- 通过Configuration().configure() 读取并解析hibernate.cfg.xml配置文件。
- 由hibernate.cfg.xml中的
读取并解析映射信息。 - 通过config.buildSessionFactory() 创建SessionFactory。
- 通过sessionFactory.openSession() 打开Sesssion。
- 通过session.beginTransaction() 创建事务Transation。
- 通过session.save()、session.update()、session.delete()、session.createQuery() 等进行持久化。
- 通过session.getTransaction().commit() 提交事务。
- 关闭Session。
第5章 Hibernate 配置
5.1.Hibernate 核心配置
Hibernate 的核心配置文件 hibernate.cfg.xml,通常放在 src/main/resources 目录下。示例如下:
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration PUBLIC |
**数据库连接关键参数 **
| 配置项 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| hibernate.connection.driver_class | JDBC驱动类(org.postgresql.Driver) |
| hibernate.connection.url | 数据库URL(jdbc:postgresql://localhost:5866/highgo) |
| hibernate.connection.username | 数据库用户名 |
| hibernate.connection.password | 数据库密码 |
| hibernate.dialect | 数据库方言(PostgreSQL10Dialect) |
Hibernate 行为配置
| 配置项 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| hibernate.show_sql | 是否在控制台输出SQL语句(true/false) |
| hibernate.format_sql | 是否格式化输出的SQL(true/false) |
| hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto | 自动生成表结构的策略(update、create、create-drop、validate) |
5.2.Hibernate 映射配置
5.2.1.注解方式
直接在实体类上使用 JPA/Hibernate 注解。
@Entity |
5.2.2.*.hbm.xml方式
通过 XML 文件定义映射。
<hibernate-mapping> |
5.2.3.主键生成策略
- increment
由HIbernate自动以递增方式生成标识符,每次增量为1。
优点:不依赖于底层数据库系统,适用于所有的数据库系统。
缺点:使用于单进程环境下,在多线程环境下很可能产生相同的主键值,而且ID必须为数值类型,比如long,int,short类型。
配置方式:
<id name="id" type="java.lang.Integer" column="id" > |
生成效果:
Hibernate: |
- identity
由底层数据库生成。
****前提条件:数据库支持自动增长字段类型,而且ID必须为数值类型,比如long,int,short类型。
配置方式:
<id name="id" type="java.lang.Integer" column="id" > |
生成效果:
Hibernate: |
说明:
Hibernate生成建表语句主键使用“generated by default as identity”进行自增。
- sequence
依赖于底层数据库的序列。
前提条件:需要数据库支持序列机制,而且ID必须为数值类型,比如long,int,short类型。
配置方式:
#方式一(推荐),指定表使用的唯一序列名 |
生成效果:
Hibernate: |
说明:
只配置主键生成策略为“sequence”,不指定序列名,会从默认序列“hibernate_sequence”生成,但多张表会出现主键跳号,如果对主键跳号无所谓,可不需要显示的指定每张表使用唯一序列名。
当Hibernate配置了“hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto”为“true”时,会自动生成显示指定的序列或默认序列,如从其它库迁移,需要数据库中创建对应的序列或者“hibernate_sequence”。
- native
native生成器能根据底层数据库的类型,自动选择合适的标识符生成器,因此非常适用于跨数据库平台开发,它会由Hibernate根据数据库适配器中的定义,自动采用identity、sequence中的一种作为主键生成方式,但是ID必须为数值类型。
配置方式:
<id name="id" type="java.lang.Integer" column="id" > |
说明:
在使用“native”主键生成器时和使用“sequence”且不指定序列名行为保持一致。
- uuid
由Hibernate基于128位唯一值产生算法,根据当前设备IP,时间,JVM启动时间,内部自增量等4个参数生成16进制数值作为主键,一般而言,利用uuid方式生成的主键提供最好的数据插入性能和数据库平台适应性。ID使用String类型,不能使用数值型。
配置方式:
<id name="id" type="java.lang.String" column="id" > |
生成效果:
Hibernate: |
第6章 Hibernate 查询语言
6.1.HQL**(Hibernate Query Language)**
HQL是一种面向对象的查询语言,与SQL类似,但操作的是实体类及其属性而非数据库表和列。HQL是大小写敏感的,除了Java类和属性名称外。
String hql = "FROM User WHERE name = :name"; |
6.2.原生SQL (Native SQL)
允许直接执行SQL语句,这对于需要利用数据库特定功能(如存储过程、特殊函数等)的情况非常有用。Hibernate允许你使用原生SQL查询,并能将结果映射到实体或DTO(数据传输对象)。
String sql = "SELECT * FROM t_user WHERE name = ?"; |
6.3.Criteria API
提供了一种类型安全的方式来构建查询,避免了字符串拼接可能带来的错误。它非常适合动态查询构造,但在Hibernate 5.2之后被注解驱动的Criteria替代,后者是JPA标准的一部分。
Criteria criteria = session.createCriteria(User.class); |
第7章 Hibernate 示例
7.1.hibernate.cfg.xml
<?xml version='1.0' encoding='utf-8'?> |
7.2.User.hbm.xml
<?xml version='1.0' encoding='utf-8'?> |
7.3.实体类 entity
@Data |
7.4.新增数据
Configuration config = new Configuration().configure(); |
7.5.查询数据
获取列表
Configuration config = new Configuration().configure(); |
根据id查询
Configuration config = new Configuration().configure(); |
7.6.删除数据
Configuration config = new Configuration().configure(); |
7.7.更新数据
Configuration config = new Configuration().configure(); |